In cnc precision manufacturing, especially for high precision cnc components, a good manufacturing process is essential to ensure dimensional accuracy, surface quality, traceability, and consistent performance.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the cnc manufacturing process, covering every key stage from raw material incoming inspection to CNC machining, surface treatment, assembly, and final inspection. By understanding this standardized process flow, buyers, engineers, and OEM partners can better evaluate a manufacturer’s technical capability and quality management level.
Overview of the Manufacturing Process Flow
The manufacturing process for cnc parts follows a structured and sequential workflow.
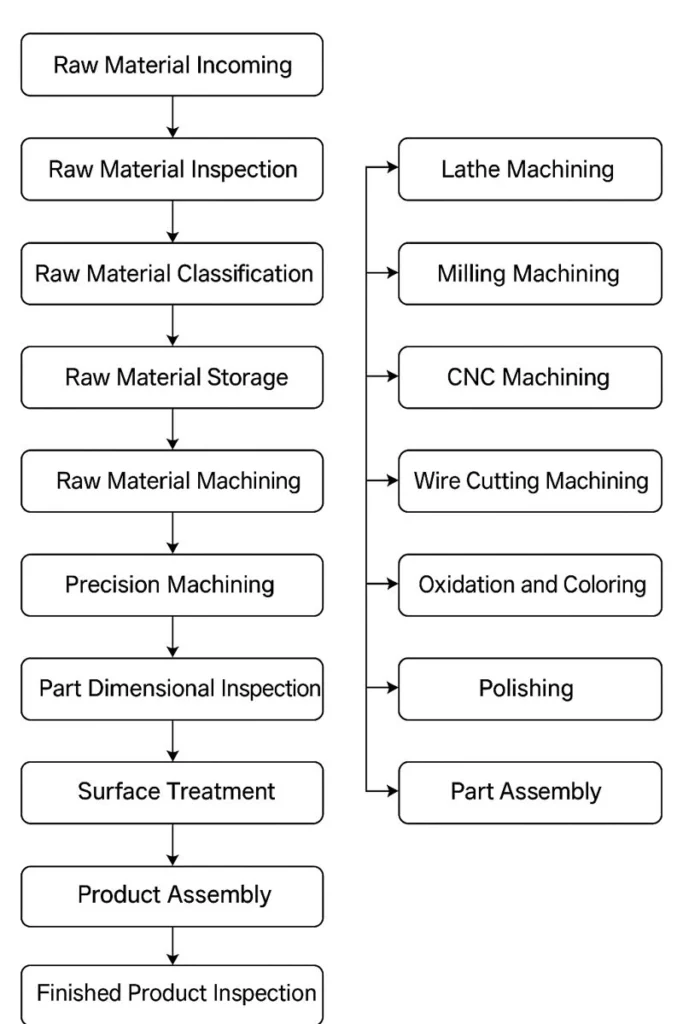
Each step is documented, controlled, and traceable to ensure stable quality and compliance with international manufacturing standards.
The complete process can be summarized as:
- Raw material incoming and inspection
- Material storage and classification
- Rough machining and CNC precision machining
- Dimensional inspection and quality control
- Surface treatment and finishing
- Product assembly
- Finished product inspection
This standardized process flow helps reduce defects, improve production efficiency, and meet the expectations of global customers in medical, industrial, and precision engineering sectors.
Raw Material Incoming and Inspection
Raw Material Incoming and FIFO Management
The manufacturing process starts with raw material incoming. All materials are received into the warehouse under a controlled system. First In, First Out (FIFO) principles are applied to ensure materials are used in the correct order, preventing long-term storage issues such as corrosion, deformation, or material aging.
Each batch of incoming material is recorded using raw material inbound and outbound records. Warehouse inspectors are responsible for verifying quantities, material identification, and basic condition before acceptance.
Incoming Inspection for Purchased Materials
For externally purchased materials, incoming inspection is a critical quality gate. Inspection is conducted based on purchase contracts and technical requirements. Relevant documents such as incoming inspection reports are generated and archived.
This step ensures that only compliant materials enter the production process, minimizing the risk of defects caused by incorrect material grade, composition, or mechanical properties. For international customers, this stage is particularly important, as it supports traceability and compliance with global quality expectations.
Raw Material Storage and Classification
Material Storage by Specification
After inspection, approved raw materials are transferred to the raw material warehouse for storage. Materials are stored by specification, size, and type to prevent mix-ups. Operation logs are maintained to track storage location and movement.
Proper storage management not only improves efficiency but also supports full traceability throughout the manufacturing process.
Material Classification Before Machining
Before machining begins, raw materials are classified according to the required machining process. Classification is based on factors such as machining sequence, CNC operations, and surface treatment requirements.
This preparation step ensures a smooth production flow and reduces handling errors, contributing to consistent product quality and stable lead times.
Rough Machining and Sequential Processing
Rough machining is typically the first production stage after material preparation. At this stage, excess material is removed to form the basic shape of the external fixation bracket.
All machining operations follow a defined sequence, ensuring that each process builds correctly upon the previous one. Operation logs are maintained to record machining progress and operator responsibility. This structured approach helps reduce rework and improves dimensional stability in later stages.
CNC Machining for Precision Manufacturing
CNC Machining Operations
CNC machining is the core process in external fixation bracket manufacturing. Using computer-controlled equipment, complex geometries and tight tolerances can be achieved with high repeatability.
CNC machining operations are carried out according to detailed production work instructions. Critical dimensions are controlled throughout the process to ensure consistency across batches. This stage is especially important for medical and precision components, where dimensional accuracy directly affects product performance and safety.
Advantages of CNC Machining
- High dimensional accuracy and repeatability
- Consistent quality for batch production
- Capability to machine complex and precise features
- Reduced human error through automated control
CNC machining enables manufacturers to meet the strict quality demands of global OEM and medical customers.
Part Dimensional Inspection and Quality Control
In-Process Dimensional Inspection
After CNC machining, part dimensional inspection is performed to verify that all critical dimensions meet drawing requirements. Precision measuring tools and inspection methods are used to ensure accuracy.
Dimensional inspection at this stage helps identify issues early, preventing defective parts from progressing to surface treatment or assembly.
Inspection Records and Traceability
Inspection results are documented using production work instructions and inspection reports. These records provide full traceability, which is essential for quality audits and international customer requirements.
Surface Treatment and Finishing Processes
Oxidation, Coloring, and Polishing
Surface treatment plays a vital role in both the functional and visual quality of cnc parts. Common surface processes include oxidation, coloring, and polishing.
These treatments improve corrosion resistance, surface appearance, and overall durability. Surface management is conducted according to standardized work instructions to ensure consistent results.
Additional Finishing Operations
Depending on product design and customer requirements, additional finishing processes may include:
- Polishing for improved surface smoothness
- Wire cutting machining for precision features
- Laser marking for product identification and traceability
Each finishing operation is controlled and documented to maintain quality consistency.
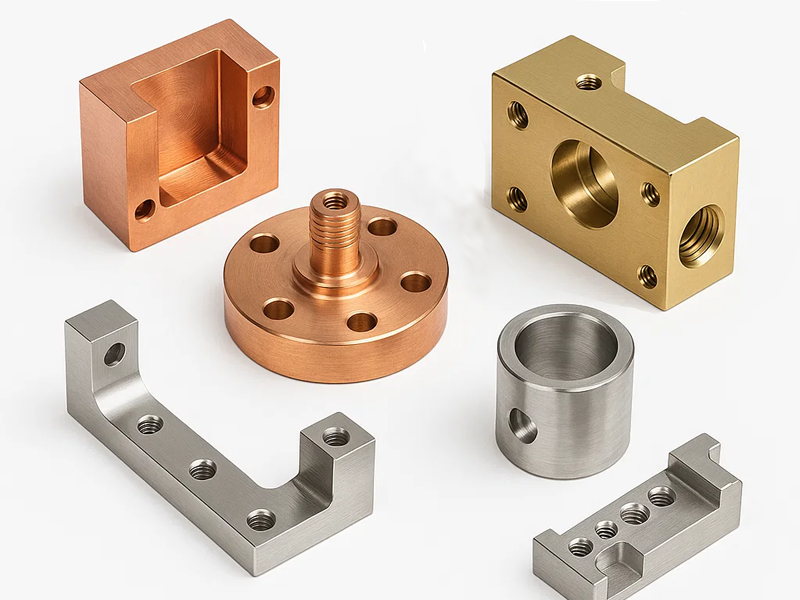

Product Assembly and Functional Integrity
Assembly Process
Once all components have completed machining and surface treatment, product assembly begins. Parts are assembled according to defined procedures to ensure proper fit and functionality.
Assembly integrity is a key control item at this stage. Operation logs are maintained to record assembly details and operator responsibility.
Importance of Controlled Assembly
A controlled assembly process ensures that the final product meets functional requirements and performs reliably in real-world applications, especially in medical environments where safety is critical.+
Final assembly plays a critical role in preventing surface defects such as stains, scratches, dents, and handling marks on finished parts. Even when CNC machining and surface treatment are completed to specification, improper assembly practices can easily compromise the final appearance and functionality of components. This is why structured process training and continuous skill development for assembly workers are essential in modern manufacturing. By strengthening employee quality training, manufacturers can ensure that operators understand proper handling methods, clean assembly environments, and standardized operating procedures. During the final assembly stage, attention to detail, use of protective fixtures, and correct tool selection significantly reduce the risk of cosmetic and functional quality issues. For CNC machining factories serving global markets such as North America and Europe, high assembly standards are not only a quality requirement but also a key factor in customer satisfaction and repeat business. Investing in professional assembly training helps reduce rework, lower scrap rates, and improve overall production efficiency, making it a vital part of any quality management system in precision manufacturing.
Finished Product Inspection
Finished product inspection is the final quality gate before delivery. Inspectors conduct comprehensive checks to verify that the product meets all specified requirements.
Inspection criteria include dimensional accuracy, surface quality, assembly integrity, and overall compliance with technical drawings. Only products that pass final inspection are approved for shipment. Inspection reports are issued and archived as part of the quality documentation system.
Why a Standardized Manufacturing Process Matters
A standardized manufacturing process offers clear benefits for global customers:
- Consistent and reliable product quality
- Reduced production risk and rework
- Full traceability from raw material to finished product
- Stable lead times and predictable performance
For buyers sourcing high precision CNC components, process transparency is a strong indicator of manufacturing capability and reliability.
Conclusion
The high precision cnc parts requires a well-structured and tightly controlled process. From raw material incoming inspection and CNC machining to surface treatment, assembly, and final inspection, every step plays a critical role in ensuring product quality and performance.
By following a standardized manufacturing process flow, manufacturers can deliver high-precision, reliable components that meet the expectations of international medical and industrial customers.
If you are looking for a CNC machining partner with strong process control and quality management, understanding their manufacturing workflow is the first step toward a successful collaboration.