Introduction
In the field of precision manufacturing, CNC turning parts are widely used across industries such as automotive, hydraulic systems, aerospace, and industrial machinery. While advanced CNC machines are essential, the quality of machined parts starts with the raw material. Even the most precise CNC operations cannot compensate for poor material quality.
For global buyers seeking reliable precision CNC turning parts, partnering with a manufacturer that implements strict material quality control is critical. This article explores how material quality impacts CNC turning accuracy, common materials used, inspection processes, defects, traceability, and batch control—all essential to ensure stable, high-quality parts.
Why Material Quality Affects CNC Turning Accuracy
Material quality directly impacts several key aspects of CNC turning:
-
Dimensional Accuracy: Variations in hardness or composition can cause inconsistent tool wear, leading to deviations from design tolerances.
-
Surface Finish: Impurities, porosity, or work-hardening tendencies affect smoothness, crucial for sealing components like BSP/BSPT threads.
-
Tool Life: High inclusions or hard spots accelerate cutting tool wear, increasing production costs and downtime.
-
Process Stability: Uniform material ensures consistent machine behavior, reducing vibrations and preventing chatter during high-speed turning.
At our CNC turning factory, we combine over 100 CNC machines, precision inspection tools, and experienced engineering staff to manage material variability and maintain precision for global orders.
Common Materials Used in CNC Turning
CNC turning parts are manufactured from a variety of metals and alloys. Each material presents unique properties, machining considerations, and applications:
1. Carbon Steel
-
Properties: Strong, versatile, and suitable for heat treatment.
-
Applications: Shafts, couplings, hydraulic components.
-
Machining Notes: Prone to work hardening in certain grades; uniform hardness is critical for dimensional stability.
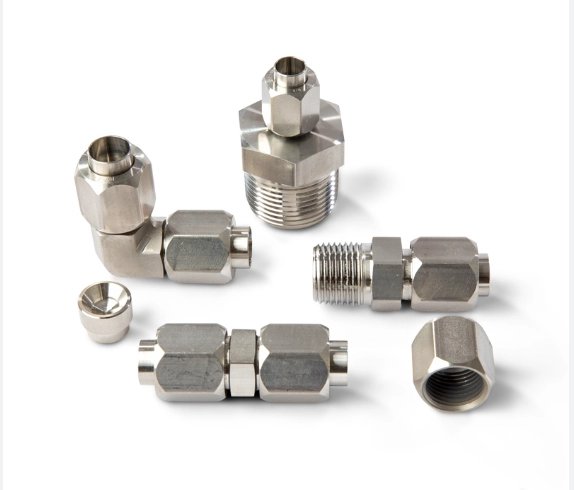
2. Stainless Steel
-
Properties: Corrosion-resistant, high strength, but more difficult to machine.
-
Applications: Medical equipment, food processing components, automotive parts.
-
Machining Notes: Requires slower feed rates to prevent surface tearing; careful control of cutting temperatures avoids hardening.

3. Brass
-
Properties: Excellent machinability, corrosion-resistant, good for threading.
-
Applications: Hydraulic fittings, connectors, decorative parts.
-
Machining Notes: Porosity or oxidation can affect sealing threads; uniform alloy composition ensures high-quality results.
4. Aluminum
-
Properties: Lightweight, easy to machine, excellent thermal conductivity.
-
Applications: Aerospace components, housings, lightweight machinery parts.
-
Machining Notes: Softness can lead to deformation; proper fixturing and tooling are essential to maintain tolerance.


Incoming Material Inspection Process (IQC)
To guarantee stable quality, most professional CNC factories implement Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
-
Visual Inspection: Detect surface scratches, oxidation, or other visible defects.
-
Chemical Analysis: Ensure the alloy composition matches specifications for the intended application.
-
Mechanical Testing: Measure hardness, tensile strength, and other mechanical properties to confirm uniformity.
-
Dimensional Verification: Confirm raw material dimensions are within acceptable tolerances for CNC setups.
-
Batch Recording: Each material lot is tagged for traceability, enabling global supply chain reliability.
Our factory uses optical projectors, hardness testers, and spectrometers to validate materials before production, reducing the risk of machining errors caused by substandard stock.
Typical Material Defects and Their Impact on Machining
Material defects can severely affect CNC turning outcomes. Below is a comparison of common defects and their impact:
| Material | Common Defects | Impact on CNC Turning | Recommended Inspection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Inclusions, hardness variation | Tool wear, tolerance deviations | Hardness testing, optical inspection |
| Stainless Steel | Work hardening, surface cracks | Poor surface finish, chatter | Hardness & surface testing, batch sampling |
| Brass | Porosity, oxidation | Thread defects, leakage | Visual inspection, dimensional check |
| Aluminum | Warping, porosity | Deformation, tolerance issues | Dimensional inspection, surface inspection |
Insight: Identifying defects early prevents costly rework and ensures that CNC turning operations remain precise and reliable for international standards.
Material Traceability and Batch Control
For global customers, material traceability is as important as material quality. Batch control enables manufacturers to:
-
Track each raw material lot from supplier to finished part.
-
Quickly identify sources of defects or inconsistencies.
-
Maintain compliance with international quality standards.
-
Provide reliable documentation for clients, especially for regulated industries like aerospace or hydraulic systems.
At our CNC factory, each material batch is labeled, documented, and linked to production orders, ensuring traceability and stable quality across large-scale orders worldwide.

Tips for Global Buyers: Ensuring CNC Turning Material Quality
-
Specify material standards: Include alloy composition, hardness, and certification requirements in purchase orders.
-
Request IQC procedures: Confirm your supplier performs incoming inspections, chemical analysis, and mechanical testing.
-
Highlight critical features: Identify key surfaces, threads, or tolerances that are highly sensitive to material variability.
-
Consider post-processing needs: Certain materials benefit from stress-relieving, polishing, or heat treatment after machining.
-
Require batch documentation: Especially important for hydraulic, automotive, and aerospace components.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: Why is material quality important in CNC turning?
A1: Material quality affects dimensional accuracy, surface finish, tool wear, and machining consistency. Poor material leads to defects, rework, and higher production costs.
Q2: Which materials are commonly used for CNC turning parts?
A2: Carbon steel, stainless steel, brass, and aluminum. Each material has unique machining properties, advantages, and challenges.
Q3: How do manufacturers inspect incoming materials?
A3: Through IQC, including visual inspection, chemical analysis, hardness testing, dimensional checks, and batch documentation.
Q4: How do material defects affect machining?
A4: Defects like porosity, inclusions, warping, or cracks can cause tool wear, poor surface finish, tolerance deviations, and even part failure.
Q5: What is material traceability and batch control?
A5: Tracking each batch from supplier to finished part ensures consistent quality, quick problem identification, and compliance with global standards.
Conclusion: Stable Materials Ensure Stable CNC Turning Quality
The foundation of high-quality CNC turning parts is stable, defect-free material. By implementing rigorous material inspection, batch control, and traceability, manufacturers can maintain precision, reduce tool wear, and achieve consistent part performance.
For global buyers, partnering with a factory that has advanced CNC capabilities, comprehensive material IQC, and robust traceability ensures that your components—whether carbon steel shafts, stainless steel fittings, brass connectors, or aluminum housings—meet the most demanding specifications.
Related topic:
Stable CNC Turning Processes for Reliable High-Precision Parts
Cutting Tool Management for CNC Turning Quality
CNC Turned Parts: How Machining Parts Manufacturers Control Accuracy and Inspection
How Engineering Drawings Affect CNC Turning Quality ?
How to CNC Turning Quality Control in cnc machinery ?