Cnc parts divide two main area :cnc turning service and cnc milling service .
Today we mainly discuss the different between cnc turning and cnc milling .
CNC turning is a precision machining process where a cutting tool removes material from a rotating workpiece to create round or cylindrical parts. “CNC” stands for Computer Numerical Control, meaning the entire cnc process is programmed and automated for high accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency.
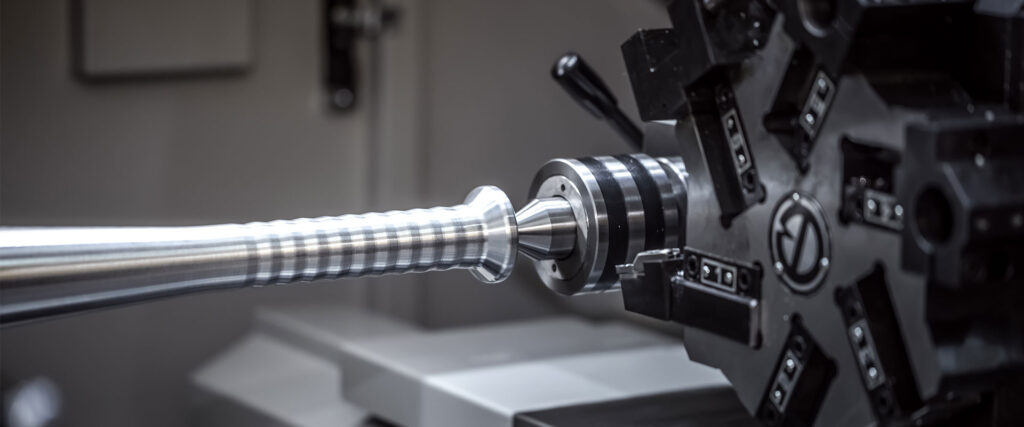
Cnc turning usually based on CAD drawing is enough to finish the cnc turned parts .
1-A bar or block of material (iron , stainless steel, brass, copper , aluminum )is clamped into a lathe. .
2-The spindle rotates the workpiece at high speed.
3-A stationary cutting tool moves along programmed paths (X/Z axes).
4-Material is gradually cut away to form the desired shape—Our company is mainly supply different type pipe fitting ,such as hydraulic fittings,elbow fittings,pneumatic fittings,bulkhead fittings etc .
CNC milling uses a rotating cutting tool that removes material from a stationary workpiece.
It can create flat surfaces, slots, pockets, contours, chamfers, holes, and highly complex 3D shapes.
If CNC turning is for round parts, CNC milling is for flat, angled, or complex parts.
A CAD model is created (3D drawing). 2D drawing is not enough to describe the cnc milling parts structure and detail.
CAM software converts it into G-code.
The workpiece is fixed on the milling table.
The tool rotates at high speed and moves along X, Y, Z axes.
Material is removed layer by layer to form the final part.

Precision Cnc turning material can be pipe , round bar, hex bar, foging parts , cold heading parts based on the cnc parts 2D drawings.
CNC turning is ideal for producing round and rotationally symmetrical components. Because the workpiece rotates at high speed, turning easily creates outer diameter , inner diameter , length , outer thread , inner thread , groove ,chamfer ,radius ,and keep with a excellent concentricity. This cnc process is widely used by cnc lathe machined suppliers in China, manufacturing hydraulic fittings, hose connectors, hose fittings , and custom precision metal components that require smooth surfaces and perfect roundnes .
CNC milling, on the other hand, is designed for cnc parts with flat surfaces, sharp edges, multi-sided features, or complex contours. Milling can produce square or polygonal shapes, pockets, slots, deep cavities, and advanced 3D geometries that cannot be achieved by turning. It is the preferred method for brackets, housings, flanges,and custom high precision cnc milling components .
CNC turning primarily uses CNC lathe machines, Swiss-type automatic bar feeders (long-bar machines), and turning–milling composite machines. These machines operate by rotating the workpiece while the cutting tools move along linear axes (X and Z).
CNC milling is performed on machining centers, which can be 3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis machines. These machines use rotating cutting tools to machine a fixed workpiece, making them suitable for producing flat surfaces, multi-face parts, pockets, cavities, and complex 3D geometries.
CNC turning tools include External turning cutter, boring cutter, threading cutter, grooving cutter and thread cutter. These tools are cost-effective, durable, and easy to replace, making them ideal for high-volume production of cylindrical, rotationally symmetrical, and threaded cnc components. China cnc factory rely on these tools for producing pipe fittings, bushings, shafts, and other high volume precision turned parts with consistent quality and efficiency. The simple tool-changing process also allows operators to manage multiple turning machines simultaneously, further improving productivity and reducing operational costs.
CNC milling uses a variety of cutting tools, such as end mills, face mills, ball nose mills, and brazed milling cutters. Compared to turning tools, milling tools are more expensive, and the tool-changing process is more complex due to multiple machining operations and multi-axis movements. These tools are essential for producing flat, multi-surface, pocketed, or complex 3D components, such as brackets, housings, flanges, and hydraulic manifolds, commonly manufactured in precision machining industry. Although the tooling cost is higher, CNC milling enables highly precise, complex shapes that turning tools cannot achieve.
Cnc lathe machines is low cost and high speed compare the cnc machining center .Cnc lathe machine is around 3-6W RMB in china , but cnc machining centre need pay 30-150w based on high accurate demand . So the tolerate for cnc lathe parts is normally around 0.02MM . Cnc maching centre is um tolerance .
And when cnc turning produce , one person can manage 3-6 sets cnc lathe machines, Cnc milling also can manage around 5-10sets . But the machine costs too high to provide competive price,and for the special cnc milled parts , every model need pay high costs mould .
Based on machine cost, speed cost , tool costs , mould costs . parts of cnc lathe is economy cost , fast delivery ,so it is suitable produce big volume cnc turning parts.
Yuhuan hongqian machinery co.,ltd is a professional cnc factory provide cnc turning service , supply different type pipe fitting .We offer CNC machining, CNC turning, stamping, welding, and forging , cold heading, assembly services, making us a one-stop solution for both standard and custom cnc machining parts.
Our factory is equipped with a complete range of production and inspection equipment to support high-precision machining and stable mass-production quality. The production workshop includes CNC turning machines, grinding machines, drilling machines, punching machines, sawing machines, and tapping machines, allowing us to handle diverse metal processing tasks from rough machining to fine finishing. To ensure dimensional accuracy, we use optical projectors, digital calipers, micrometers, and depth gauges for routine inspections. In addition, we maintain a full set of advanced laboratory and verification tools, including a 2.5D optical measuring projector, hardness tester, metallographic analyzer, cutting machine, laser marking machine, and salt-spray corrosion test chamber. With this combination of machining capability and comprehensive quality-control equipment, we can guarantee consistent precision, reliable durability, and high-level product performance for every batch produced.
CNC turning excels at producing cylindrical, rotationally symmetrical components due to its rotating workpiece and linear tool movement. The following operations are best suited for turning and either cannot be efficiently performed on milling machines or would be extremely costly:
External cylindrical turning
Internal hole turning
Concentricity up to 0.01 mm or better
Milling machines cannot produce truly round shapes and often create faceted or polygonal surfaces instead.
External threads (male)
Internal threads (female)
Pipe threads (NPT/G/R/BSP/BSPT ETC)
Metric or imperial threads (UNF/UN)
Fine-pitch threads
Milling can cut threads, but precision is lower and efficiency is slower; turning ensures stable, accurate threads.
Motor shafts
Valve stems
Long bar components
Milling cannot handle long, rotating shafts efficiently or maintain uniform material removal.
Deep boring and smooth internal surfaces
Turning tools can bore deep holes with excellent surface finish.
Milling deep holes is prone to tool vibration and inconsistent material removal.
Conical surfaces
Rounded transitions
Rotationally symmetric ball surfaces
Milling can attempt these shapes, but toolpaths are complex, speed is slower, and surface finish is usually inferior.
Summary Table – Turning Capabilities
| Capability | CNC Turning | CNC Milling |
|---|---|---|
| Perfect roundness | ✅ | ❌ |
| Long shaft machining | ✅ | ❌ |
| High-precision threading | ✅ | ❌ (not precise) |
| Deep boring | ✅ | ❌ |
| Rotational curves (taper/arc) | ✅ | ❌ |
CNC milling offers rotating cutting tools and multi-axis movement, allowing it to machine any shape, including non-rotational and complex geometries. These operations are only feasible with milling:
Flat surface machining
Vertical faces, top faces, chamfers, and planar features
Turning cannot produce flat surfaces or multiple faces.
Square, rectangular, or polygonal shapes
Blocks, multi-sided profiles, square flanges, housings, covers
Turning cannot create non-cylindrical shapes.
Cavities, pockets, and slots
Hydraulic manifold cavities
Motor housing slots
Recessed areas or pockets
Turning cannot achieve multi-axis pocketing.
Side holes, eccentric holes, or non-central holes
Turning can only machine holes along the centerline.
Complex 3D geometries (5-axis)
Turbine blades
Freeform curves
3D aesthetic components
Aerospace parts
Turning cannot machine freeform 3D surfaces.
Summary Table – Milling Capabilities
| Capability | CNC Milling | CNC Turning |
|---|---|---|
| Flat surfaces | ✅ | ❌ |
| Square/rectangular shapes | ✅ | ❌ |
| Cavities/pockets/slots | ✅ | ❌ |
| Multi-face machining | ✅ | ❌ |
| Eccentric/side holes | ✅ | ❌ |
| Complex 3D structures | ✅ | ❌ |
CNC Turning = The World of Cylinders
Ideal for shafts, round parts, threaded components, deep holes, and high concentricity.
CNC-turned components include:
Bulkhead fittings
Hydraulic fittings & adapters
Pneumatic fittings & quick connectors
Plumbing fittings / pipe connectors
Hose barb fittings
Elbow connectors (rotational body types)
Threaded adapters & reducer fittings
Grease fitting adapters / lubrication connectors
Hex nuts, union nuts, round nuts
Bolts, threaded rods, precision screws
Bushings, sleeves, spacers, standoffs
Shafts, pins, couplings
Automobile turning parts & mechanical hardware

CNC Milling = The World of Flats and Complex 3D Shapes
Required for multi-face, flat, pocketed, square, or highly complex components that turning machines cannot produce.
CNC-milled components include:
Hydraulic manifold block / pneumatic manifold block
Valve body (cavity type)
Machined brackets / mounting blocks / support plates
Aluminum housings and enclosures
Base plates, fixture plates, steel plates
Flanges and flange plates
Heat sinks and cooling components
Tooling fixtures and jigs
3D contour parts and complex machined components
Electronics shell, CNC-milled covers and faceplates
Automotive structural parts and mechanical components
Machine tool accessories and custom fixture blocks
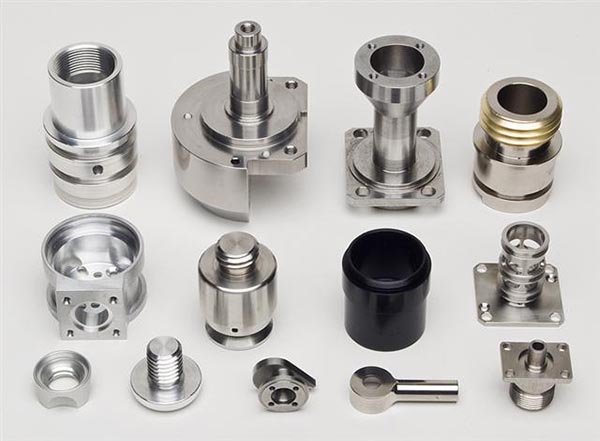

CNC turning and CNC milling each play a vital role in modern precision manufacturing. Turning excels at producing round, rotational parts with high efficiency, while milling delivers the flexibility needed for flat surfaces, complex geometries, and multi-axis machining. By combining both processes, manufacturers can achieve the perfect balance of accuracy, speed, and cost-effectiveness. Whether your project requires simple shafts or highly engineered 3D components, choosing the right machining method ensures better performance, tighter tolerances, and a more reliable final product.