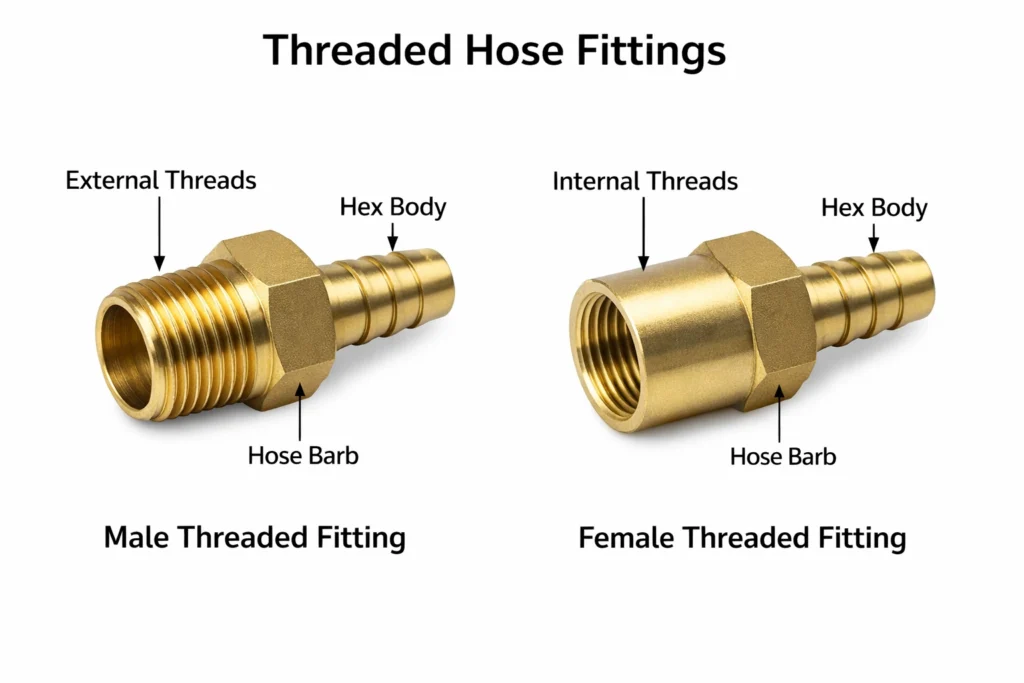
What is a hose fittings?
A hose fitting is a precision-engineered component used to connect hoses to pipes, valves, pumps, or other fluid control equipment, ensuring a secure and leak-free flow of liquids or gases.Hose fittings can be manufactured from various materials, but the material selection must match the working pressure, temperature, fluid media, and operating environment. In industrial applications, hose fittings are commonly made from carbon steel, stainless steel, brass, and aluminum, while alloy steel or special materials are used for high-pressure or corrosive conditions. Using an unsuitable material may lead to leakage, corrosion, reduced service life, or system failure.
Which type material could be used in hose fittings ?
| Material | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Brass | Excellent corrosion resistance and conductivity; provides a tight, leak-proof seal. | Low to medium pressure gas, water, and fuel lines. |
| Carbon Steel | High tensile strength and durability; cost-effective for heavy-duty use. | High-pressure hydraulic systems and industrial machinery. |
| Stainless Steel | Superior resistance to chemicals, heat, and rust; high hygiene standards. | Food processing, medical, chemical, and marine industries. |
Hoses vs. Tubes and Pipes: What’s the Difference?
Hoses, tubes, and pipes are all used to transfer fluids or gases, but they serve different purposes in industrial systems. Hoses are flexible components designed to accommodate movement, vibration, and misalignment, making them ideal for hydraulic and pneumatic applications. Tubes are rigid or semi-rigid, manufactured with tight dimensional tolerances and defined by outer diameter and wall thickness, commonly used in precision fluid control systems. Pipes, on the other hand, are rigid and specified by nominal size, focusing on fluid transport capacity rather than dimensional accuracy, and are widely used in fixed piping and infrastructure systems. Understanding these differences is essential when selecting the correct connection method and fittings for reliable and safe operation.
What is tube fitting ?
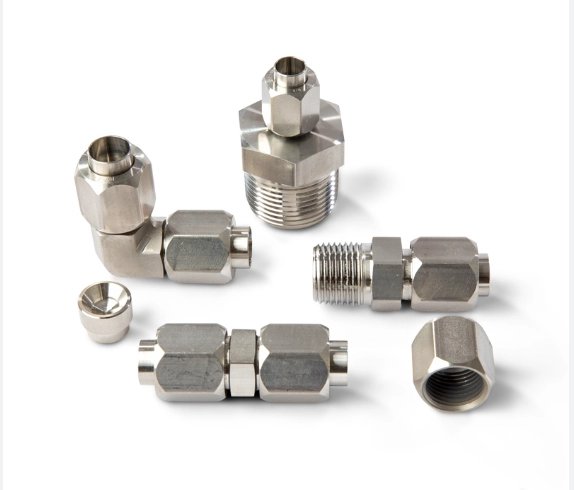

What is pipe fitting ?
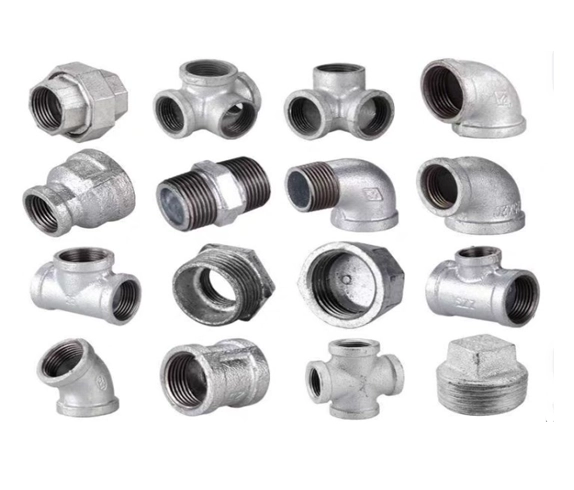

Types of hose fittings
Hose fittings are crucial components in hydraulic, pneumatic, and fluid transfer systems, ensuring secure connections and leak-free operation. Selecting the right hose fitting type enhances system efficiency, safety, and durability. Below is a detailed classification of hose fittings for industrial applications in taizhou,zhejiang .
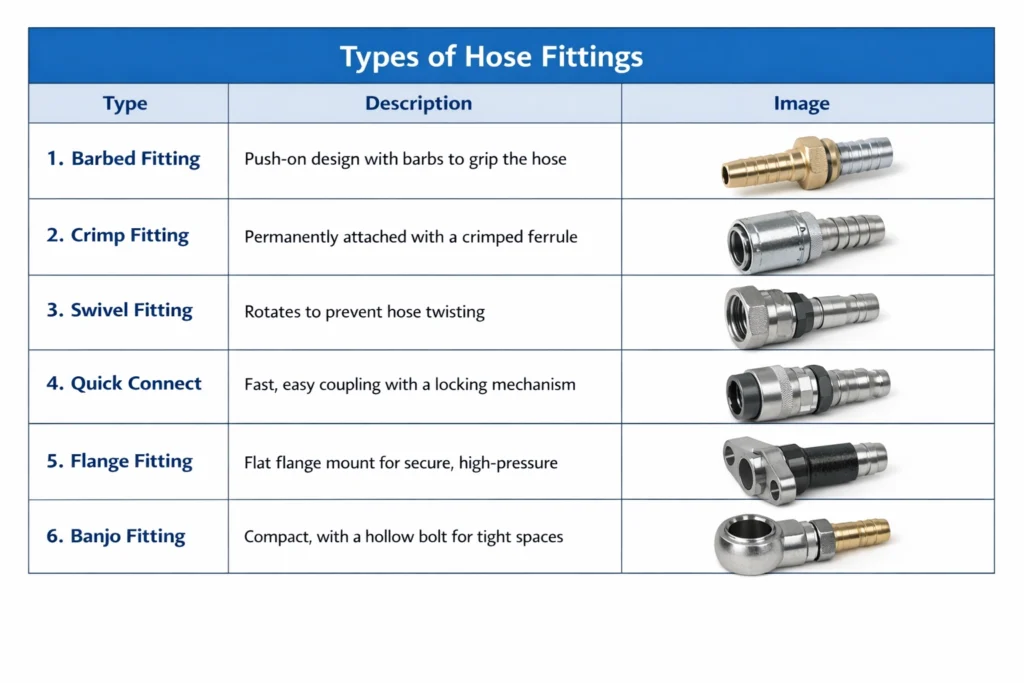
1. Threaded Fittings
Threaded fittings are widely used for high-pressure applications. They provide a tight and reliable connection between hoses and pipes, preventing leaks and ensuring long-term stability. Common types include NPT (National Pipe Thread), BSP (British Standard Pipe), and metric threaded fittings.
2. Barbed Fittings
Barbed fittings are ideal for flexible hoses in low- to medium-pressure systems. The barbed design grips the hose internally, often used with clamps for added security. They are commonly applied in chemical transfer, water systems, and pneumatic lines.
3. Quick Couplings (Quick Connects)
Quick couplings allow fast and tool-free connection and disconnection of hoses. They are highly convenient for maintenance or systems that require frequent hose changes. These fittings are often used in hydraulic equipment, air compressors, and industrial machinery.
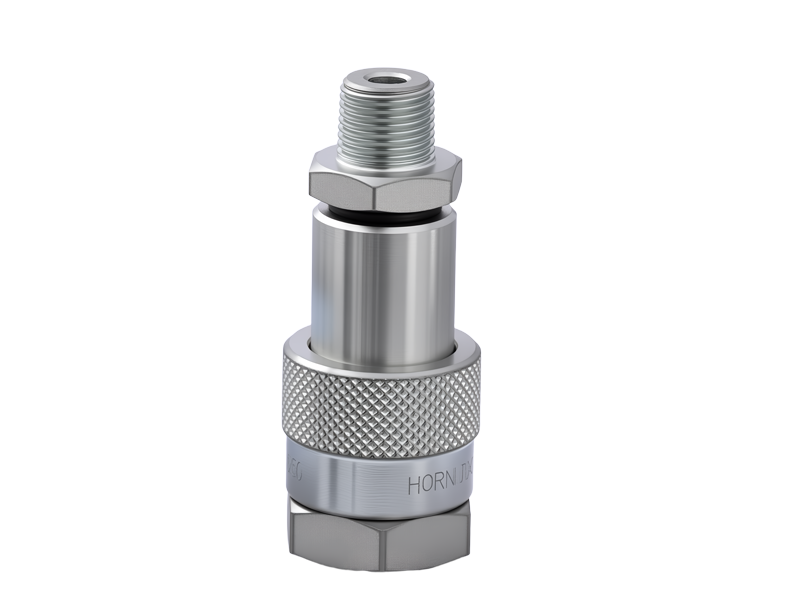

4. Crimped Fittings
Crimped fittings are permanent solutions for high-pressure hoses. Using a hydraulic crimping machine, the fitting is securely attached to the hose, providing excellent leak resistance and durability. These are commonly applied in heavy machinery, automotive hydraulics, and industrial fluid systems.
5. Flanged Fittings
Flanged fittings connect hoses to pumps, valves, or large-diameter pipes. They provide strong mechanical support and are ideal for high-flow systems in chemical plants, water treatment, and manufacturing facilities.
By understanding these different types of hose fittings, engineers, procurement specialists, and maintenance teams in china can select the most suitable fittings, reduce downtime, and optimize system performance. Choosing high-quality local suppliers ensures compliance with safety standards and reliable long-term operation.
How to use a hose fitting?
Hose fittings are essential components in hydraulic systems, pneumatic systems, CNC machinery, and industrial equipment. Proper installation ensures a leak-free, secure connection and prolongs the lifespan of both hoses and machinery.
1. Choose the Right Hose Fitting
Select the fitting type that matches your hose and application:
-
Threaded fittings (NPT, BSP, metric) for high-pressure piping.
-
Barbed fittings for flexible hoses in fluid or air systems.
-
Quick-connect fittings for fast assembly in industrial lines.
-
Crimp fittings for permanent, high-pressure connections.
2. Prepare the Hose
Cut the hose cleanly with a sharp tool, remove debris, and slightly lubricate if necessary. Proper preparation ensures a snug and reliable fit, especially in hydraulic and CNC applications.
3. Attach the Fitting
-
Barbed fittings: Insert fully and secure with a hose clamp.
-
Threaded fittings: Wrap male threads with PTFE tape and tighten carefully.
-
Quick-connect fittings: Push until the fitting clicks.
-
Crimp fittings: Use a crimping tool to secure the sleeve evenly.
4. Test for Leaks
Slowly run water, oil, or air through the system, and check the connection. Tighten or adjust as needed to ensure industrial-grade reliability.
5. Maintenance and Safety Tips
-
Avoid bending hoses sharply near fittings.
-
Inspect clamps or crimped fittings regularly.
-
Replace damaged hoses immediately to prevent downtime in factories, workshops, or hydraulic plants.
How to measure size and thread ?
1-Size inspection
Once the required type of hose fitting has been determined, the next crucial step is selecting the proper size. Correct sizing is vital for ensuring a secure and leak-free connection—using an oversized or undersized fitting can lead to poor sealing, improper connection, or complete incompatibility. Hose fitting sizes are defined by the inside diameter (ID) and outside diameter (OD) of the corresponding connections, typically measured in inches (in) or millimeters (mm). Specifically, a fitting intended for a hose with a 2-inch OD is rated as a 2-inch OD fitting. The inside diameter refers to the hollow portion of the hose, while the outside diameter accounts for the full thickness of the hose wall. Properly matching these dimensions guarantees optimal performance and reliability in hydraulic or fluid systems.
Follow is the detail way for check the outer diameter and inner diamter by caliper tool .
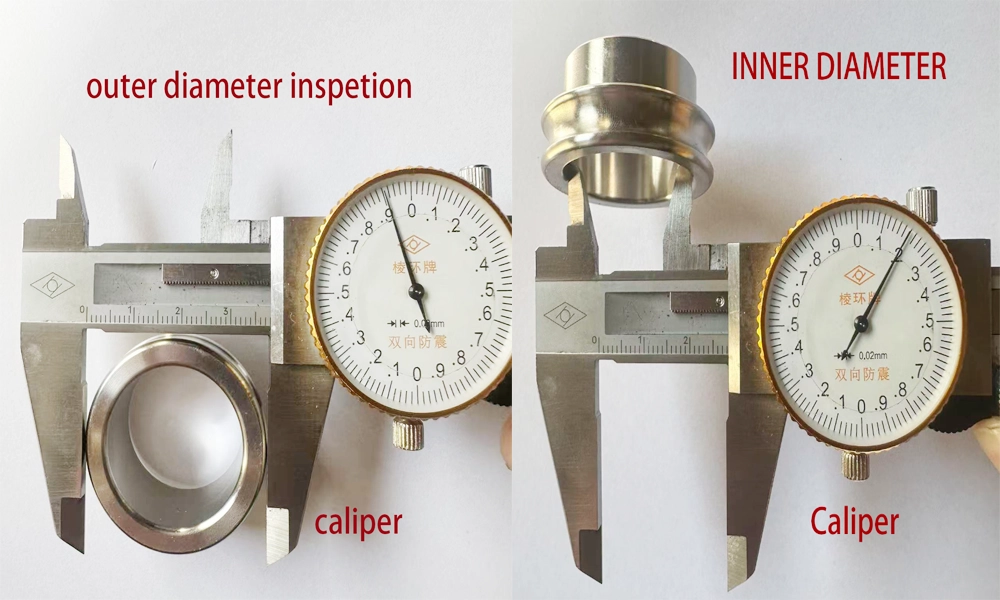
Hose fitting
2-Thread size inspecation .
How to Properly Identify and Check Hose Fitting Threads ?
To ensure a leak-free connection, identifying a hose fitting requires more than just a quick glance. While using a thread pitch gauge is a fundamental first step to verify the thread pitch (mm) or TPI (threads per inch) and the thread angle (55° vs. 60°), it is often insufficient on its own.
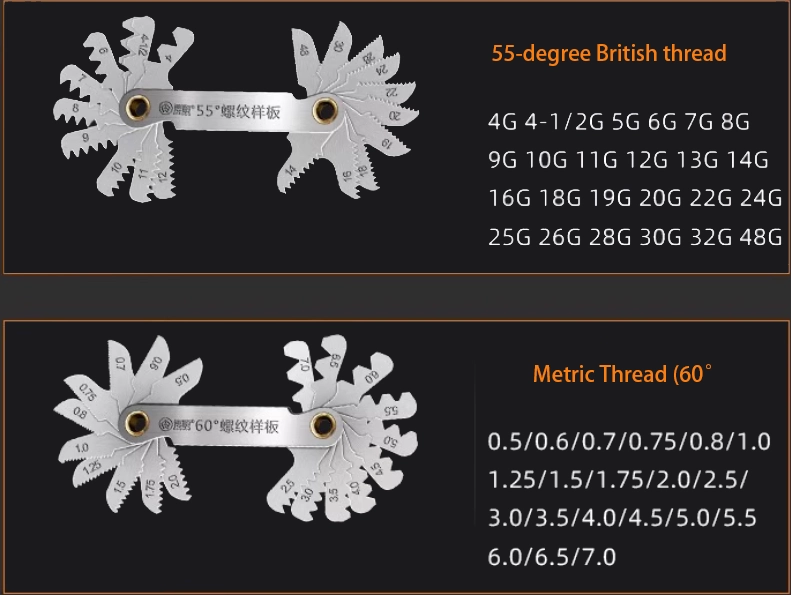
A professional inspection should follow these three steps:
-
Identify the Thread Type: Use a pitch gauge to determine if the thread is Metric (60°), Whitworth (55°), or UN/UNF (60°).
-
Measure the Diameter: Use digital calipers to measure the Outside Diameter (O.D.) of male threads or Inside Diameter (I.D.) of female threads. This helps confirm the exact size of the fitting and avoids confusion between similar pitches.
-
Determine if the Thread is Tapered or Parallel: Observe if the diameter changes along the length of the thread. This distinguishes between standards like BSPT (tapered) and BSPP (parallel), which is vital for selecting the correct mating part.
- For a professional cnc turning parts manufacture , we have the profile projector can check the thread outer diameter , inner diameter , thread pitch , Thread taper for a more convenient and accurate results.Especially for NPT , BSPT , choose the thread gauge is hard to know the thread tapper .
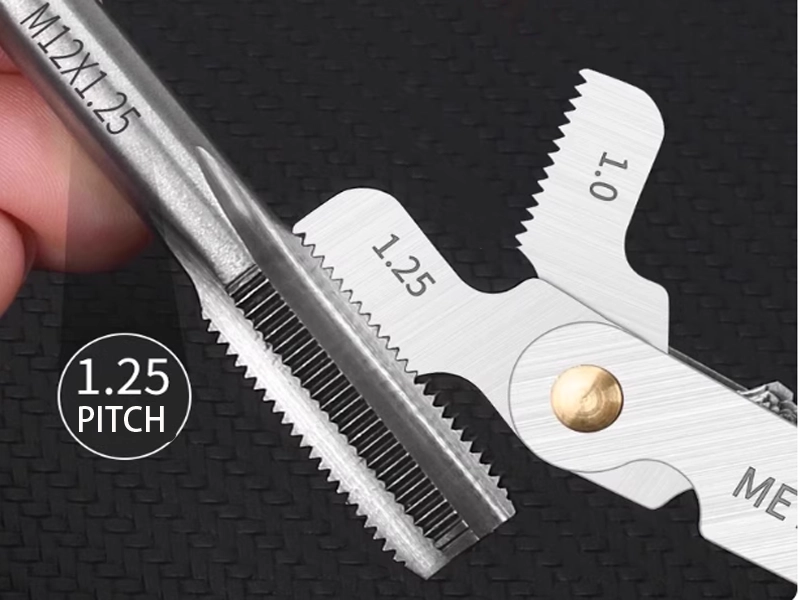

Function
Divide by the different function , there are sitill have many types hose fitttings . We make up in follow .
| Name | Description | photo |
|---|---|---|
| Elbow fitting | Used to change the direction of flow between two pipes, commonly available in 90° and 45° angles to navigate tight spaces. |  |
| wye | A Y-shaped fitting with a 45° branch designed to reduce flow turbulence and friction compared to a standard tee. |  |
| T connecotor | A T-shaped fitting used to combine or divide fluid flow, featuring a 90° branch relative to the main line. |  |
| plug | A male-threaded fitting used to close off the end of an internally threaded pipe or component to stop flow. |  |
| Adapter fitting | A versatile component used to connect two pipes or hoses with different sizes, thread types, or connection standards. |  |
| nipple | A short piece of pipe with male threads at both ends, used to connect two female-threaded fittings or valves. |  |
| screw plug | A threaded fastener used to seal or plug holes in blocks, manifolds, or tanks, often featuring a hex or socket head. |  |
Summary: The Essentials of Hose Fitting Selection and Maintenance
Hose fittings are precision components vital for secure, leak-free fluid transfer in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. Unlike rigid pipes or tubes, hoses offer flexibility for movement and vibration. Selecting the correct fitting—whether Threaded, Barbed, Quick-coupling, or Crimped—is the first step toward system reliability. Material choice is equally critical: Brass offers corrosion resistance for low-pressure lines, Carbon Steel provides strength for heavy-duty hydraulics, and Stainless Steel ensures hygiene and chemical resistance for extreme environments.
Accuracy in sizing and thread identification is paramount. Professional inspection involves using digital calipers for diameter measurement and pitch gauges to distinguish between 55° Whitworth and 60° Metric profiles. For complex tapered threads like NPT or BSPT, advanced manufacturers utilize profile projectors to ensure precise taper and pitch accuracy. Following a rigorous process of preparation, correct attachment, and regular maintenance prevents costly leaks and downtime, ensuring optimal performance in demanding industrial applications.