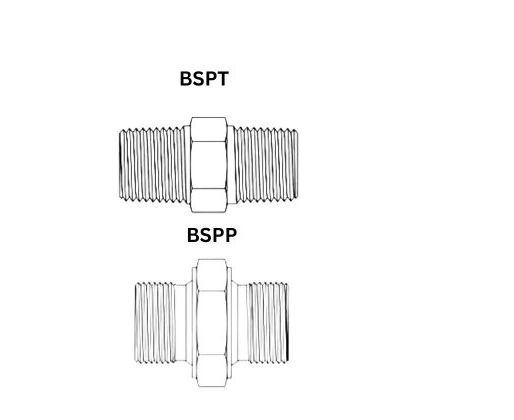
Pipe threads play a critical role in fluid and gas systems across industries such as hydraulics, pneumatics, automotive manufacturing, oil & gas, and general industrial equipment. Among the most widely used thread standards outside North America are BSPT and BSPP threads, both derived from the British Standard Pipe system.
Despite their similar names, BSPT and BSPP threads are not interchangeable in most applications. Misunderstanding their differences can lead to leakage, pressure failure, or costly rework.
This guide provides a clear and practical explanation of BSPT vs BSPP threads, covering what BSPP stands for, how BSP differs from BSPP, whether BSPT and BSPP are compatible, and what BSPT threads are typically used for in real-world industrial systems.
What Is BSP Thread?
BSP stands for British Standard Pipe, a standardized pipe thread system originally developed in the United Kingdom and now widely used across Europe, Asia, the Middle East, and many international industrial markets.
BSP threads are characterized by a 55-degree Whitworth thread angle, with rounded crests and roots, which distinguishes them from other pipe thread standards such as NPT. Due to this geometry and standardization, BSP threads are commonly specified for:
-
Hydraulic fittings
-
Pneumatic systems
-
Fluid transfer and pipe connections
-
Industrial machinery and equipment
-
Plumbing and low- to medium-pressure gas systems
The BSP thread system consists of two primary thread forms, each serving a different sealing purpose:
-
BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) – parallel threads that require a sealing washer, O-ring, or gasket
-
BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper) – tapered threads that seal through thread interference
Understanding the functional and structural differences between BSPP and BSPT is critical for achieving proper sealing, avoiding leakage, and ensuring long-term connection reliability in industrial applications.
What Does BSPP Stand For?
BSPP stands for British Standard Pipe Parallel.
As the name suggests, BSPP threads are parallel (straight) along their entire length. The thread diameter does not change from the beginning to the end of the fitting.
Key Characteristics of BSPP Threads
- Parallel male and female threads
- Do not seal on the threads themselves
- Require an additional sealing method
- Typically sealed using:
- O-rings
- Bonded seals
- Flat washers
- Machined sealing faces
BSPP threads are commonly designated with the letter “G” in technical drawings and standards.
What Is BSPT Used For?
BSPT stands for British Standard Pipe Tapered.
Unlike BSPP, BSPT threads are tapered, Taper 1:16, meaning the thread diameter gradually decreases along the length of the thread. This taper allows the threads to compress against each other as they are tightened, creating a pressure-tight seal.
Common Applications of BSPT Threads
BSPT threads are widely used in:
- Gas distribution systems
- High-pressure fluid lines
- Industrial piping
- Oil and fuel transfer
- Compressed air systems
Because BSPT threads seal through metal-to-metal contact, they are often used together with:
- PTFE tape
- Thread sealant compounds
BSPT threads are typically marked with the letter “R” in standards such as ISO 7.
BSPP vs BSPT: Design and Sealing Differences
Although BSPP and BSPT share the same thread angle and pitch system, their sealing principles are fundamentally different.
Structural Differences
Detailed Comparison: BSPP vs BSPT Threads
| Feature | BSPP (Parallel) | BSPT (Tapered) |
|---|---|---|
| Full name | British Standard Pipe Parallel | British Standard Pipe Taper |
| Thread form | Parallel (straight) thread | Tapered thread |
| Taper | None | 1:16 taper (≈ 1.789° half angle) |
| Thread angle | 55° Whitworth | 55° Whitworth |
| Crest & root shape | Rounded | Rounded |
| Sealing method | Seals via O-ring, bonded seal, or flat washer | Seals by thread interference |
| Pressure capability | Medium to high (depends on seal type) | Medium pressure |
| Thread diameter | Constant along length | Gradually decreasing |
| Engagement length | Fixed | Progressive tightening |
| Risk of over-tightening | Low | Higher |
| Ease of assembly | Easy, repeatable | Requires torque control |
| Interchangeability | Not self-sealing | Not compatible with BSPP |
| Typical standards | ISO 228-1 | ISO 7-1 |
| Common markings | G | R (external), Rc / Rp (internal) |
| Typical applications | Valves, adapters, manifolds | Pipe fittings, hydraulic ports |
| Common regions | Europe, Asia, Middle East | Europe, Asia, Middle East |
Sealing Behavior
- BSPP threads rely on an external sealing surface, making them ideal for applications where controlled torque and repeated assembly are required.
- BSPT threads create a seal through tightening force and thread deformation, making them suitable for permanent or semi-permanent connections under pressure.
Are BSPT and BSPP Compatible?
This is one of the most frequently asked questions in industrial sourcing, fluid systems, and mechanical engineering. Many engineers and buyers wonder whether BSPT (British Standard Pipe Tapered) threads can be connected to BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) threads without problems.
Short Answer:
BSPT and BSPP threads are generally not compatible.
Detailed Explanation:
-
Thread Geometry Differences
-
BSPT threads are tapered: The diameter of the thread decreases along its length, which allows the threads to create a tight interference fit when screwed together. This taper is essential for pressure sealing.
-
BSPP threads are parallel: The diameter remains constant along the length. BSPP threads rely on an additional sealing mechanism, usually an O-ring or washer, to prevent leaks.
-
-
Sealing Mechanisms Are Different
-
BSPT: Achieves sealing through thread interference, meaning the threads themselves form a metal-to-metal seal under pressure.
-
BSPP: Requires a separate sealing element (O-ring, washer, or gasket) because the threads alone cannot provide a leak-proof connection.
-
-
Risks of Mixing BSPT and BSPP
-
A BSPT male threaded component screwed into a BSPP female thread may initially feel tight due to friction.
-
However, because the threads do not match geometrically and the sealing mechanisms differ, the connection cannot reliably withstand pressure.
-
This mismatch can lead to leaks, thread damage, or even system failure, especially in high-pressure applications.
-
-
Practical Guidance
-
High-pressure applications: Always use BSPT for pressure-tight connections.
-
Low-pressure or non-critical systems: BSPP is sufficient, but never attempt to mix BSPT and BSPP threads.
-
Always check specifications: Refer to ISO 7-1 / BS 21 standards to ensure thread type and sealing method are correctly matched.
-
Are There Any Exceptions?
In some cases, a BSPT male fitting may screw into a BSPP female port, but this does not guarantee a reliable seal. Any apparent fit is purely mechanical and should not be considered safe for pressure systems unless a proper sealing solution is engineered.
For professional applications, adapters specifically designed to convert BSPT to BSPP should always be used.
Are BSP and BSPP the Same?
Another common source of confusion is the terminology itself.
BSP is not the same as BSPP.
- BSP is the overall thread system
- BSPP is one specific type within the BSP system
- BSPT is the other main type
In practical terms:
- Saying “BSP thread” without specifying P or T is incomplete
- Always confirm whether a fitting is BSPP or BSPT before manufacturing or sourcing components
Clear specification is especially important in CNC machining, custom fittings, and international procurement.
How to Identify BSPP vs BSPT Threads
Correct identification prevents costly mistakes during installation or production.
Visual Inspection
- BSPP threads appear straight with no visible taper
- BSPT threads visibly narrow toward the end
Measurement
- Measure the thread diameter at different points
- BSPP will remain consistent
- BSPT will show gradual reduction
Thread Gauges and Standards
- Use a BSP thread gauge to confirm pitch and angle
- Check part markings or technical drawing.
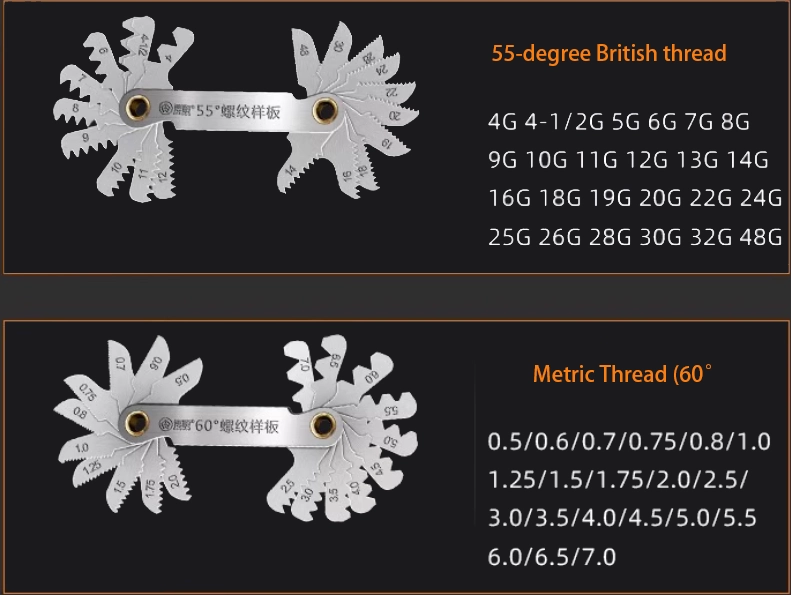

Professional inspection tools are especially important in precision CNC-machined fittings and hydraulic components.
Common BSPP Thread Sizes
| Marking | Nominal Size | Major Diameter (mm) d=D | Pitch (mm) p | TPI | Pitch Diameter (mm) d2=D2 | Minor Diameter (mm) d3 | Thread Height (mm) H1 | Drill Size (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1/8 | 1/8" | 9.728 | 0.907 | 28 | 9.147 | 8.566 | 0.581 | 8.70 |
| G1/4 | 1/4" | 13.157 | 1.337 | 19 | 12.301 | 11.445 | 0.856 | 11.60 |
| G3/8 | 3/8" | 16.662 | 1.337 | 19 | 15.806 | 14.950 | 0.856 | 15.00 |
| G1/2 | 1/2" | 20.955 | 1.814 | 14 | 19.793 | 18.631 | 1.162 | 19.00 |
| G5/8 | 5/8" | 22.911 | 1.814 | 14 | 21.749 | 20.587 | 1.162 | 20.75 |
| G3/4 | 3/4" | 26.441 | 1.814 | 14 | 25.279 | 24.117 | 1.162 | 24.50 |
| G7/8 | 7/8" | 30.201 | 1.814 | 14 | 29.039 | 27.877 | 1.162 | 28.00 |
| G1 | 1" | 33.249 | 2.309 | 11 | 31.770 | 30.291 | 1.479 | 30.50 |
| G1-1/8 | 1-1/8" | 37.897 | 2.309 | 11 | 36.418 | 34.939 | 1.479 | 35.00 |
| G1-1/4 | 1-1/4" | 41.910 | 2.309 | 11 | 40.431 | 38.952 | 1.479 | 39.50 |
| G1-3/8 | 1-3/8" | 44.323 | 2.309 | 11 | 42.844 | 41.365 | 1.479 | 41.50 |
| G1-1/2 | 1-1/2" | 47.803 | 2.309 | 11 | 46.324 | 44.845 | 1.479 | 45.00 |
| G1-3/4 | 1-3/4" | 53.746 | 2.309 | 11 | 52.267 | 50.788 | 1.479 | 51.00 |
| G2 | 2" | 59.614 | 2.309 | 11 | 58.135 | 56.656 | 1.479 | 57.00 |
| G2-1/4 | 2-1/4" | 65.71 | 2.309 | 11 | 64.231 | 62.752 | 1.479 | 63.00 |
| G2-1/2 | 2-1/2" | 75.184 | 2.309 | 11 | 73.705 | 72.226 | 1.479 | 72.50 |
| G2-3/4 | 2-3/4" | 81.534 | 2.309 | 11 | 80.055 | 78.576 | 1.479 | 79.00 |
| G3 | 3" | 87.884 | 2.309 | 11 | 86.405 | 84.926 | 1.479 | 85.50 |
| G3-1/4 | 3-1/4" | 93.98 | 2.309 | 11 | 92.501 | 91.022 | 1.479 | 91.00 |
| G3-1/2 | 3-1/2" | 100.33 | 2.309 | 11 | 98.351 | 97.372 | 1.479 | 97.75 |
| G3-3/4 | 3-3/4" | 106.68 | 2.309 | 11 | 105.201 | 103.722 | 1.479 | 104.00 |
| G4 | 4" | 113.03 | 2.309 | 11 | 111.55 | 110.072 | 1.479 | 110.50 |
| G4-1/2 | 4-1/2" | 125.73 | 2.309 | 11 | 124.251 | 122.772 | 1.479 | 123.00 |
| G5 | 5" | 138.43 | 2.309 | 11 | 136.951 | 135.472 | 1.479 | 136.00 |
Common BSPT Thread Sizes
| Nominal Size (NPS) | Threads per Inch (TPI) | Major Diameter (OD, mm) | Pitch Diameter (PD, mm) | Minor Diameter (ID, mm) | Taper | Pitch (P, mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3/8" | 19 | 16.662 | 15.806 | 14.95 | 1:16 | 1.337 |
| 1/2" | 14 | 20.955 | 19.793 | 18.631 | 1:16 | 1.814 |
| 3/4" | 14 | 26.441 | 25.279 | 24.117 | 1:16 | 1.814 |
| 1" | 11 | 33.249 | 31.770 | 30.291 | 1:16 | 2.309 |
| 1-1/4" | 11 | 41.910 | 40.431 | 38.952 | 1:16 | 2.309 |
| 1-1/2" | 11 | 47.803 | 46.324 | 44.845 | 1:16 | 2.309 |
| 2" | 11 | 59.614 | 58.125 | 56.656 | 1:16 | 2.309 |
| 2-1/2" | 11 | 75.184 | 73.705 | 72.226 | 1:16 | 2.309 |
| 3" | 11 | 87.884 | 86.405 | 84.926 | 1:16 | 2.309 |
| 4" | 11 | 113.030 | 111.551 | 110.072 | 1:16 | 2.309 |
| 5" | 11 | 138.430 | 136.951 | 135.472 | 1:16 | 2.309 |
| 6" | 11 | 163.830 | 162.351 | 160.872 | 1:16 | 2.309 |
Typical Industrial Use Cases
BSPP Applications
- Hydraulic hose fittings
- Valves and manifolds
- Equipment requiring frequent maintenance
- Systems using O-ring face sealing
BSPT Applications
- Gas and fuel pipelines
- Industrial plumbing
- Compressed air systems
- Fixed installations requiring self-sealing threads
Choosing the correct thread type improves safety, service life, and system efficiency.
BSP Threads in Global Manufacturing and CNC Machining
BSP threads remain a dominant standard in:
- The UK and Europe
- Asia-Pacific manufacturing
- Middle Eastern industrial projects
For CNC machining suppliers and OEM manufacturers, accurate BSPP and BSPT thread production requires:
- Correct tooling and thread profiles
- Tight tolerance control
- Consistent inspection procedures
Thread accuracy is especially critical in high-pressure and safety-critical components.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Assuming BSPP and BSPT are interchangeable
- Ignoring sealing requirements
- Over-tightening BSPP fittings
- Using incorrect thread sealant
- Failing to specify thread type in drawings or purchase orders
Avoiding these mistakes reduces downtime and improves system reliability.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between BSPT and BSPP threads is essential for engineers, buyers, and manufacturers working with fluid and gas systems.
To summarize:
- BSP is the overall British Standard Pipe system
- BSPP stands for British Standard Pipe Parallel
- BSPT stands for British Standard Pipe Tapered
- BSPP and BSPT are not inherently compatible
- BSPT is commonly used where pressure-tight sealing is required
- BSPP is preferred where controlled sealing and reusability are important
Correct thread selection ensures safety, performance, and long-term operational success in industrial applications worldwide
Related topic :