In industrial fluid power systems, the terms hose fitting and hose coupling are frequently used interchangeably, which often leads to confusion during product selection and system design. While both components are used to connect hoses within hydraulic, pneumatic, and industrial applications, they serve different functional purposes. Understanding the difference between hose fittings and hose couplings is essential for ensuring system reliability, safety, and maintenance efficiency.
Understanding Hose Fittings in Industrial Applications
What Is a Hose Fitting?
A hose fitting is a general industrial metal component used to connect a hose to another element of a fluid system, such as a pipe, valve, pump, manifold, or cylinder. Hose fittings are typically designed for permanent or semi-permanent installation, where long-term sealing performance and pressure resistance are critical.
In hydraulic and industrial environments, hose fittings are usually installed by crimping, threaded connections, or mechanical clamping, depending on the system pressure and application requirements.
Key Functions of Hose Fittings
Hose fittings play a critical role in:
-
Maintaining leak-free sealing under high pressure
-
Providing mechanical strength to hose assemblies
-
Ensuring compatibility with thread standards and system interfaces
-
Supporting long service life in demanding industrial conditions
Because of these requirements, hose fittings are commonly manufactured from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, brass, or alloy steel, often with surface treatments like zinc plating, nickel plating, or passivation.
Common Types of Hose Fittings
Typical hose fitting designs include:
-
Threaded hose fittings (NPT, BSP, BSPT, JIC, ORFS, metric threads)
-
Crimped hydraulic hose fittings
-
Barbed hose fittings for low-pressure systems
-
Flange hose fittings used in high-flow hydraulic circuits
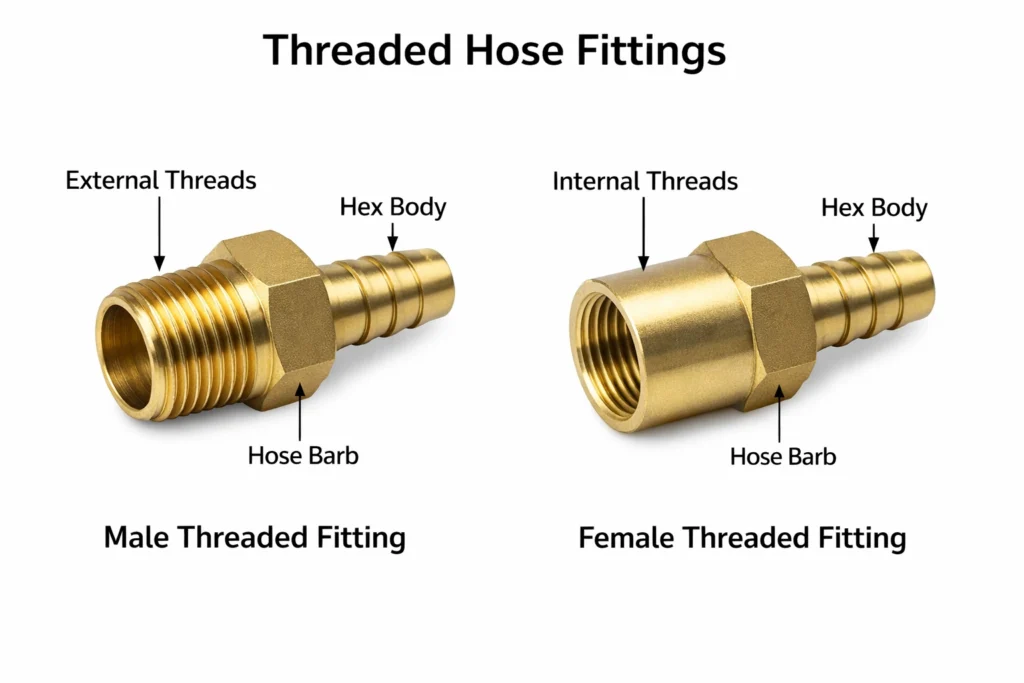
These fittings are widely used in fixed hydraulic systems, CNC machinery, industrial equipment, and automotive manufacturing.
Understanding Hose Couplings and Their Purpose
What Is a Hose Coupling?
A hose coupling is a specialized type of hose fitting designed specifically for quick connection and disconnection. Unlike standard hose fittings, hose couplings are intended to be connected and disconnected repeatedly without compromising sealing performance.
Most hose couplings consist of a male and female component, allowing hoses to be attached or removed quickly during maintenance, equipment changeovers, or temporary installations.
Why Hose Couplings Are Used
Hose couplings are commonly selected when:
-
Equipment requires frequent hose replacement
-
Downtime must be minimized
-
Systems are designed with modularity and flexibility
-
Maintenance access is limited or time-sensitive
Because of these advantages, hose couplings are widely used in hydraulic service equipment, construction machinery, industrial cleaning systems, and mobile equipment.
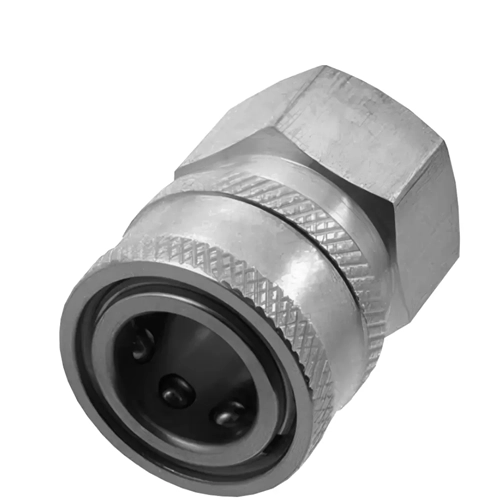

Common Types of Hose Couplings
Typical hose coupling designs include:
-
Hydraulic quick couplings
-
Camlock (cam and groove) couplings
-
Push-to-connect hose couplings
Each type is designed to balance ease of use, sealing reliability, and pressure performance.

Hose Fitting vs Hose Coupling: Key Technical Differences
Installation and Connection Method
The primary difference between hose fittings and hose couplings lies in how they are installed and used.
Hose fittings are generally installed once and left in place for long-term operation, while hose couplings are designed for repeated connection and disconnection.
Structural Design
-
Hose fittings are typically single-piece components that form a fixed connection.
-
Hose couplings consist of two mating parts that lock together using mechanical or spring-loaded mechanisms.
Maintenance and System Flexibility
Hose couplings significantly improve system flexibility by allowing hoses to be removed without tools or system disassembly. In contrast, hose fittings prioritize durability and pressure resistance over convenience.
| Feature | Hose Fitting | Hose Coupling |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | General term, includes all types of hose connections | A specialized type of hose fitting |
| Connection Method | Fixed or long-term installation | Quick connect / disconnect |
| Structure | Single-piece or crimped design | Male and female components paired together |
| Typical Applications | Fixed hydraulic systems, high-pressure systems | Frequent disconnection, modular systems |
Study the tablepress, we can clear all hose couplings are hose fittings, but not all hose fittings are hose couplings.
When to Choose a Hose Fitting or a Hose Coupling
Applications Best Suited for Hose Fittings
Hose fittings are the preferred solution when:
-
The hose connection is intended to be permanent
-
The system operates under high pressure
-
Maximum sealing reliability is required
-
Hose removal is infrequent or unnecessary
Applications Best Suited for Hose Couplings
Hose couplings are more appropriate when:
-
Hoses must be connected and disconnected frequently
-
Equipment maintenance is routine
-
Modular or mobile systems are used
-
Reducing downtime is a priority
US vs EU Thread Standards for Hose Fittings and Couplings
After understanding what hose fittings and hose couplings are, the next critical step in designing or purchasing a hydraulic or industrial hose system is ensuring thread compatibility. Incorrect thread selection can lead to leaks, installation failures, downtime, or costly returns. In this article, we will explore the differences between US and EU thread standards, their technical characteristics, and key considerations for procurement and system design.
Common US Thread Types
In North American systems, the most widely used thread standards for hose fittings and couplings are:
NPT (National Pipe Taper): Tapered threads that form a mechanical seal when tightened, thread tapper 1:16.
NPS (National Pipe Straight): Straight threads typically combined with an O-ring or gasket for sealing.
JIC (Joint Industry Council): 37° flared belong to hydraulic fittings used for hydraulic systems, offering high-pressure reliability.Usually UNF threads .
| JIC Size | Thread Size (inches) | Threads Per Inch (TPI) | Dash Size | Tap Drill Size (inches) | Flare Diameter (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8″ | 5/16-24 UNF | 24 | -2 | 0.272 | 0.184 |
| 3/16″ | 3/8-24 UNF | 24 | -3 | 0.332 | 0.250 |
| 1/4″ | 7/16-20 UNF | 20 | -4 | 0.391 | 0.313 |
| 5/16″ | 1/2-20 UNF | 20 | -5 | 0.453 | 0.391 |
| 3/8″ | 9/16-18 UNF | 18 | -6 | 0.510 | 0.469 |
| 1/2″ | 3/4-16 UNF | 16 | -8 | 0.682 | 0.625 |
| 5/8″ | 7/8-14 UNF | 14 | -10 | 0.810 | 0.750 |
| 3/4″ | 1 1/16-12 UNF | 12 | -12 | 0.955 | 0.938 |
| 1″ | 1 5/16-12 UNF | 12 | -16 | 1.195 | 1.188 |
| 1 1/4″ | 1 5/8-12 UNF | 12 | -20 | 1.535 | 1.469 |
| 1 1/2″ | 1 7/8-12 UNF | 12 | -24 | 1.776 | 1.750 |
| 2″ | 2 1/2-12 UNF | 12 | -32 | 2.276 | 2.406 |
- Taper vs straight design affects sealing and torque
- Sealing methods: metal-to-metal or O-ring
- Pressure ratings vary by material and size, typically suitable for high-pressure hydraulic applications
Technical Features
Typical Application
- Thread angle: 60° for NPT
- Hydraulic systems and machinery in North America
- Industrial equipment designed for US standards
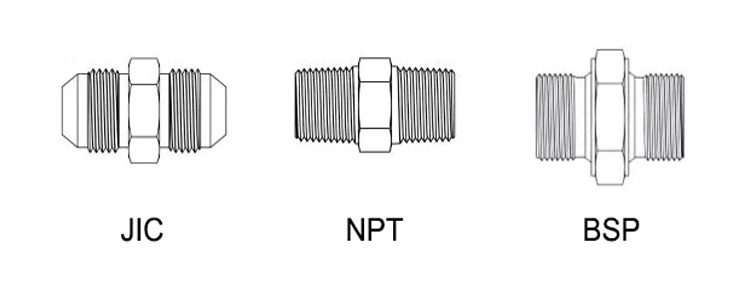
EU Thread Standards Overview
Common EU Thread Types
In European systems, BSP threads are the most common:
BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel): Straight threads, sealed with O-rings or gaskets
BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper): Tapered threads forming mechanical seals
Technical Features
- Thread angle: 55°
- Thread pitch and profile differ from US threads
- Pressure ratings comparable but must be verified against manufacturer specifications
- Common materials include stainless steel, brass, and alloy steel
Typical Applications
- European industrial equipment and machinery
- Systems requiring compliance with ISO/BSP standards
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between hose fittings and hose couplings, as well as the differences between US and EU thread standards, is essential for designing reliable and efficient fluid power systems. Selecting the right connection type ensures leak-free performance, mechanical strength, and ease of maintenance, while proper thread compatibility prevents installation issues and operational downtime. Whether you are working with permanent hydraulic systems or modular, quick-change applications, carefully choosing hose fittings or couplings according to your system requirements and regional standards will enhance both safety and productivity in industrial, automotive, and hydraulic environments.