Air hose fittings are essential components in pneumatic systems, providing secure and leak-free connections between air compressors, tools, and hoses. Whether you are setting up a home workshop, an automotive garage, or an industrial production line, understanding the different types of hose fittings is crucial for safety, efficiency, and durability. This guide will cover everything you need to know about air hose fittings, including quick connect hose fittings, thread sizes, and tips for choosing the best fittings for your needs.
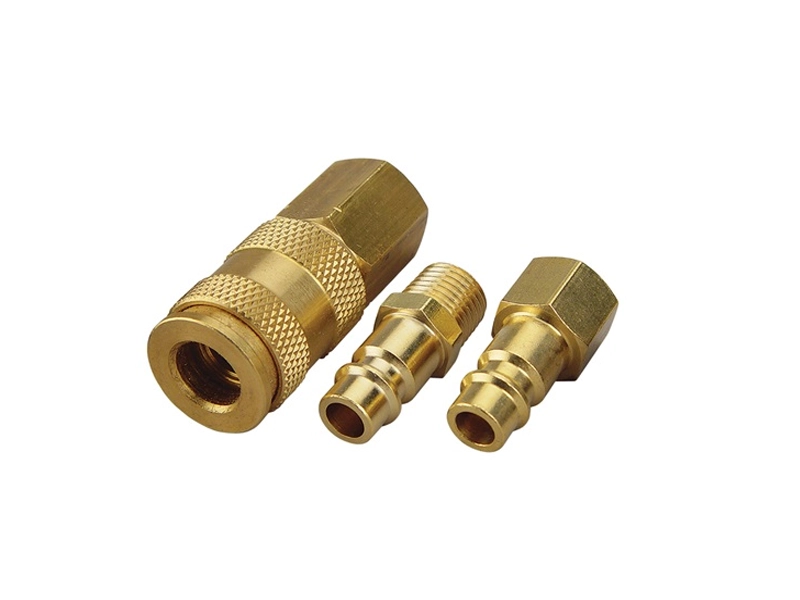

Types of Air Hose Fittings
When it comes to connecting air hoses, there are several types of fittings available, each designed for specific applications and standards. The most common types include quick connect hose fittings, threaded fittings, and specialty fittings.
Quick Connect Hose Fittings
Quick connect hose fittings, also known as quick disconnect fittings, are widely used in pneumatic systems for their convenience and speed. These fittings allow users to connect and disconnect hoses from tools or compressors without the need for wrenches or complex tools. They come in different standards such as Industrial, Automotive, ARO, and V-style, each with unique locking mechanisms and color codes for easy identification. Industrial style fittings typically feature a durable metal sleeve and are suitable for heavy-duty applications, while Automotive and ARO styles are optimized for workshop and garage use.
Threaded Hose Fittings
Threaded hose fittings, including NPT (National Pipe Thread), BSP (British Standard Pipe), and metric threads, provide a secure, leak-proof connection through threaded coupling. These fittings are ideal for permanent installations and applications requiring high-pressure tolerance. Threaded fittings are available in both male and female configurations and must match the hose diameter and tool connection to ensure proper sealing.
Specialty Hose Fittings
In addition to quick connect and threaded fittings, there are specialty hose fittings designed for specific functions. Examples include reusable fittings for temporary setups, blow gun fittings for compressed air cleaning, and tire inflator fittings for automotive applications. Choosing the right specialty fitting ensures maximum efficiency and prevents unnecessary wear or leaks in the system.
Thread Sizes for Air Hose Fittings
Selecting the correct thread size is critical when working with air hose fittings. Common sizes include 1/4″, 3/8″, and 1/2″ NPT, with BSP or metric equivalents in some regions. Proper thread sizing ensures compatibility between the hose, tool, and compressor, preventing leaks and reducing wear. Measuring thread size accurately requires basic tools like a caliper or thread gauge, and it’s essential to consider both the inner and outer diameter as well as the thread pitch.
Choosing the Best Air Hose Fittings
When selecting air hose fittings, consider several factors:
-
Material and Durability: Brass, stainless steel, and high-quality aluminum are common materials, offering corrosion resistance and longevity.
-
Leak-Proof Design: Fittings with O-rings or other sealing mechanisms provide reliable air containment.
-
Ease of Use: Quick connect hose fittings offer superior convenience for frequent tool changes, while threaded fittings excel in permanent setups.
-
Application Requirements: Evaluate pressure ratings, hose diameter, and compatibility with tools and compressors to ensure optimal performance.
For home workshops and DIY enthusiasts, lightweight brass quick connect fittings often suffice. Automotive garages benefit from standardized Industrial or Automotive quick connect fittings, while industrial facilities may require heavy-duty stainless steel fittings capable of handling high pressure and continuous operation.
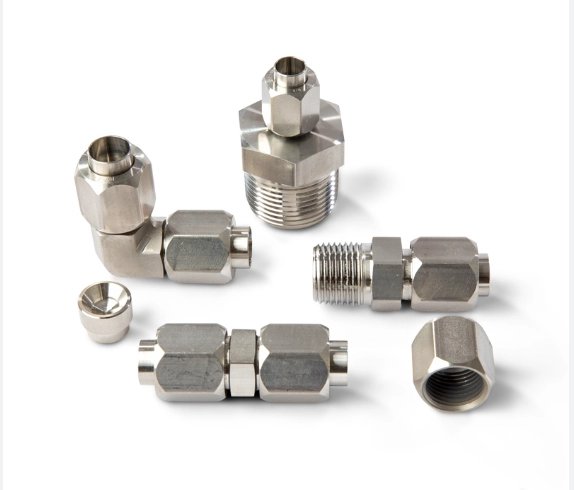

Installation and Maintenance Tips
Proper installation and maintenance are essential to extend the life of your hose fittings. Always match the fitting type and thread size to the hose and tool specifications, avoid over-tightening, and inspect fittings regularly for signs of wear, corrosion, or leaks. Using the correct sealant on threaded fittings and replacing damaged O-rings can prevent costly downtime and maintain system efficiency.
Conclusion
Air hose fittings, whether quick connect hose fittings or standard threaded fittings, are a critical part of any pneumatic system. Choosing the right type, thread size, and material ensures safety, efficiency, and longevity in both workshop and industrial environments. By understanding the differences between fitting types and following best practices for installation and maintenance, users can optimize performance and reduce the risk of air leaks or equipment failure.
For businesses and individuals in North America seeking reliable air hose fittings, it is recommended to source products from reputable suppliers that offer clear specifications and support multiple fitting standards. Proper selection and care of hose fittings not only improve system performance but also enhance workplace safety and productivity.